

Literature on DIPs is mostly focused on product compatibility and standardization, licensing, software versioning and upgrade ( Wu & Chen, 2007) few studies have addressed the NPD process of DIPs ( Rowley, 2016). This singular case study contributes for a greater comprehension of the NPD process of DIPs. The following research question, then, is specified: how does the development of DIPs occur in that firm, and what are the critical success factors (CSFs) for their development? Accordingly, its purpose is to investigate the NPD process of DIPs and as well as its CSFs. The firm under study, ABC Online-Marketing GmbH (from now on, ABC), was chosen for its mature know-how in digital product development processes, but also because of access to valuable data and information. To get an in-depth comprehension of structured and unstructured processes and dynamics of NPD involving DIP, a case study was selected as a research initiative.

This is the case for obtaining a clearer understanding of organizational activities and processes, leading to the successful creation and introduction of DIPs, especially since most of the literature focuses on tangible goods. As a result, NPD activities, once discrete and restricted to specific departments/areas, have progressively become part of an integrated process involving multiple areas and even groups outside the organization ( Kim, Kim, Sawng, & Lim, 2018 Zahay, Hajli, & Sihi, 2018 Zhan & Tan, 2020). Sustainable competitive advantage depends not only on efficiency, but also on constant renewal of product portfolio and innovation ( Pullen, Weerd-Nederhof, Groen, Song, & Fisscher, 2009 Santos-Vijande, López-Sánchez, & Rudd, 2016 Tomkovick & Miller, 2000 Woodcock, Mosey, & Wood, 2000 Nicholas, Ledwith, & Perks, 2011 Healy, O’Dwyer, & Ledwith, 2018 Zhan & Tan, 2020). This scenario may not only be favorable for firms and organizations engaged with digital information products (DIPs), but also for entrepreneurs focused on developing and selling DIPs (online courses, eBooks, webinars, etc.).Īlike, the continuous need to market new products as a basis for competitive advantage has resulted in a growing interest in NPD within DIP activities, both in managerial and academic settings. The global market size for corporate e-learning was valued at US$64.4bn in 2019 and is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate of 9.16% by 2025 ( Cision PR Newswire, 2020).
#Inmr from scan full#
The full terms of this licence maybe seen at Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Published in Innovation & Management Review.
#Inmr from scan license#
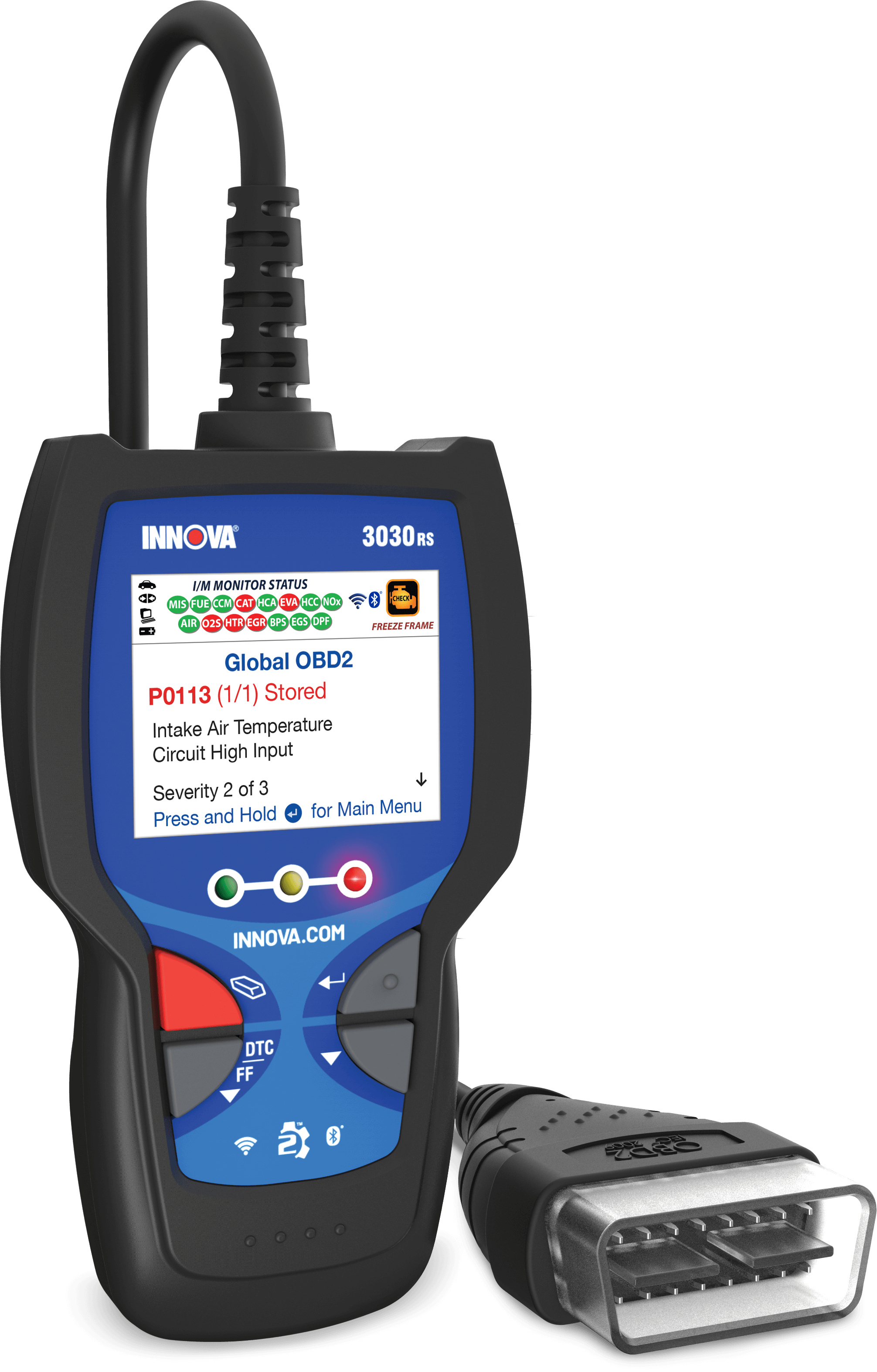
(SAE).Copyright © 2021, Pascal Keller and Afonso Lima License Spatial auto-encoder (AE) and an adaptation of a patch-fed siamese auto-encoder

We illustrate this trade-off on Parkinson's disease (PD) anomalyĭetection comparing the performance of two anomaly detection models based on a Image, while potential inconveniences are the loss of global structural Input data and to capture local and fine anomaly patterns distributed in the Unsupervised pipelines which have both the advantage to increase the number of Good candidate approaches are patch-based Tasks such as the identification of barely visible brain lesions, especially Image analysis applications, their use remains difficult when targeting subtle
#Inmr from scan pdf#
Authors: Verónica Muñoz-Ramírez (GIN,LJK), Nicolas Pinon (CREATIS), Florence Forbes (LJK), Carole Lartizen (CREATIS), Michel Dojat (GIN) Download PDF Abstract: Although neural networks have proven very successful in a number of medical


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
